INTRODUCTION:
Constitution: Is a book of rules, implied or express, to run a country, and it includes the briefings of all the facilities available for the people of the country. The constitution is known to define the fundamental rights of a person of a country. It also includes the rules that a government, its officials and citizens have to follow for maintaining peace, prosperity and progress.Here, I shall discuss the great old constitution of the USA, and its importance.

The constitution of the USA is as old as about two centuries. It was created on September 17, 1787 and it is still in force, due to equal balance of powers of government among legislative, executive and judicial system. Mostly, one body of system of government does not overlap or interefere in the matters of other body. Each body and its functions are cleared defined in thr constitution. This process of balance of powers, that is also called separation of powers, has helped many other countries including Pakistan to form a basic structure of a government. It is suffice to say that USA is a strong country, due to its constitution, as all the rights of the people are protected in it, and that the representatives of government work hard to maintain the top constitution intact and impacted.

Copy of first Constitution of USA
There are seven (7) Articles of the US constitution, which are described as under: –
Article I – The Legislative Branch. The principal mission of the legislative body is to make laws. It is split into two different chambers – the House of Representatives and the Senate. Congress is a legislative body that holds the power to draft and pass legislation, borrow money for the nation, declare war and raise a military. It also has the power to check and balance the other two federal branches.
Article II – The Executive Branch. This branch of the government manages the day-to-day operations of government through various federal departments and agencies, such as the Department of Treasury. At the head of this branch is the nationally elected President of the United States.The president swears an oath to ‘faithfully execute’ the responsibilities as president and to ‘preserve, protect and defend the Constitution of the United States’. Its powers include making treaties with other nations, appointing federal judges, department heads and Ambassadors, and determining how to best run the country and run military operations.
Article III – The Judicial Branch. Article III outlines the powers of the federal court system. Determines that the court of last resort is the US Supreme Court and that the US Congress has the power to determine the size and scope of those courts below it. All judges are appointed for life unless they resign due to bad behavior. Those facing charges are to be tried and judged by a jury of their peers.
Article IV – The States. This article defines the relationship between the states and the federal government. The federal government guarantees a republican form of government in each state, protects the nation and the people from foreign or domestic violence, and determines how new states can join the Union. It also suggests that all the states are equal to each other and should respect each other’s laws and the judicial decisions made by other state court systems.
Article V – Amendment. Future generations can amend the Constitution if the society so requires it. Both the states and Congress have the power to initiate the amendment process.
Article VI – Debts, Supremacy, Oaths. Article VI determines that the US Constitution, and all laws made from it are the ‘supreme Law of the Land’, and all officials, whether members of the state legislatures, Congress, judiciary or the Executive have to swear an oath to the Constitution.
Article VII – Ratification. This article details all those people who signed the
Constitution, representing the original 13 states.
Here, I shall discuss Article V i.e. Amendment, which says that
“on the Application of two thirds of the Legislatures of the several States, [Congress] shall call a
Convention for proposing amendments.
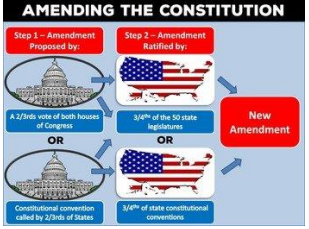
The convention can propose amendments, whether Congress approves of them or not. Those proposed amendments would then be sent to the states for ratification. In the history of US constitution, there are total 27 amendments, and the most recent was made in 1992. The Constitution has evolved time to time to meet the changing needs of a modern society profoundly different from the eighteenth-century world in which its creators lived. The following steps must be completed for an amendment proposed by Congress to be added to the United States Constitution.
Step 1. Passage by Congress. Proposed amendment language must be approved by a two-thirds vote of both houses.
Step 2. Notification of the states. The national archivist sends notification and materials to the governor of each state.
Step 3. Ratification by three-fourths of the states. Ratification of the amendment language adopted by Congress is an up-or-down vote in each legislative chamber. A state legislature cannot change the language. If it does, its ratification is invalid. A governor’s signature on the ratification bill or resolution is not necessary.
Step 4. Tracking state actions. Proposed amendments must be ratified by three-fourths of the states in order to take effect. Congress may set a time limit for state action. The official count is kept by Office of the Federal Register at the National Archives. Legislatures must return specific materials to show proof of ratification.
Step 5. Announcement. When the requisite number of states ratify a proposed amendment, the archivist of the United States proclaims it as a new amendment to the U.S. Constitution. Actual certification is published immediately in the Federal Register and eventually in the United States Statutes at-Large.
Resultantly, it is concluded that the constitution of USA is difficult and time taking process.